Aptos
2025年09月19日更新
5 人订阅
原价:
¥ 2.2
限时优惠
专栏简介
Aptos 开发实战:从环境搭建到第一个 Hello World
Aptos 开发指南:在 JetBrains 编辑器中配置运行、编译、测试与发布部署,实现更高效开发
Aptos 区块链智能合约入门:使用 Move 实现消息存储与检索
Aptos Move 语言中的变量管理与内存所有权机制详解
Aptos Move 编程语言中的四大基础类型解析:UINT、STRING、BOOL 与 ADDRESS
深入解读 APTOS-MOVE 中的 Vector 向量核心特性与操作
深入理解APTOS-MOVE中的函数修饰符:核心概念与应用
深入解读 Aptos Move 的 Struct 特性与四大能力
Aptos Move 控制流解析:IF、WHILE与LOOP的深入解读
Aptos Move 模块的特性与实操指南:模块引用与作用域管理
Aptos Move 模块的发布与交互:完整指南
深入理解 Aptos Move 中的 Object 创建与管理
深入探索 Aptos Move:Object 配置与实操指南
使用 Aptos Move 实现随机数生成:从 AIP-41 到实战操作
Aptos Move 实践指南:构建并部署同质化代币水龙头 (FA Faucet)
Aptos Move NFT 项目实操指南:从开发到部署全流程解析
Aptos Move 开发入门:从环境搭建到合约部署全流程实录
Aptos Move 入门:从零到一的合约开发与测试实战
Move 语言核心:布尔逻辑与地址类型的实战精解
深入 Aptos Move:从public到friend,函数可见性详解
Aptos Move 编程:for、while 与 loop 循环的实战详解
Aptos Move 安全编程:abort 与 assert! 错误处理实战
Aptos Move 实战:基础运算与比较逻辑的实现与测试
Aptos Move 性能优化:位运算与移位操作实战
Aptos Move 实战:as 关键字与整数类型转换技巧
Aptos Move DeFi 实战:从零构建流动性池兑换逻辑
Aptos Move 实战:用 signer 实现合约所有权与访问控制
Aptos Move 核心安全:& 与 &mut 引用机制详解
Aptos Move 实战:全面掌握 SimpleMap 的增删改查
Aptos Move 入门:掌握链上资源(Resource)的增删改查
Aptos Move 深度实践:用嵌套数据结构构建链上金银储备系统
Aptos Move 实操:如何用 Tables 构建一个链上房产管理系统
Aptos Move 实操:如何用 Tables 构建一个链上房产管理系统
Aptos Move实战:5分钟掌握链上向量(Vector)核心操作
Aptos Move 实战:从零构建一个链上价格预言机 (含源码和测试)
Aptos Move 全栈实战:构建链上价格预言机与客户端交互
Move 智能合约实战:在 Aptos 上构建你的首个 Web3 应用
深入解读 APTOS-MOVE 中的 Vector 向量核心特性与操作
- 寻月隐君
- 发布于 2024-09-11 10:45
- 阅读 3144
深入解读APTOS-MOVE中的Vector向量核心特性与操作在区块链智能合约开发中,数据结构是处理复杂操作的关键组件之一。在AptosMove语言中,Vector是一种重要的数据结构,它类似于其他编程语言中的数组,支持对相同类型数据的高效存储和操作。本篇文章将深入探讨Aptos
深入解读 APTOS-MOVE 中的 Vector 向量核心特性与操作
在区块链智能合约开发中,数据结构是处理复杂操作的关键组件之一。在 Aptos Move 语言中,Vector 是一种重要的数据结构,它类似于其他编程语言中的数组,支持对相同类型数据的高效存储和操作。本篇文章将深入探讨 Aptos Move 中 Vector 的核心特性,以及如何通过增删改查等常见操作灵活使用这一结构。
本文详细介绍了 Aptos Move 语言中的 Vector 数据结构,包括其基础概念和常见操作方法。通过示例代码展示了如何在 Move 模块中执行对 Vector 的插入、删除、修改、访问等操作,帮助开发者全面掌握这一关键数据结构的使用技巧。文章还通过单元测试验证了每个操作的正确性,为开发者提供了实践参考。
APTOS-MOVE VECTOR 向量核心特性 1 基础概念 Vector(向量)类似其它语言中的数组, 内部存储的是同一类型的数据。
| 语法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| vector[] | 空数组 |
| vector[e1,...,en] | 具有同类型元素的数组 |
实操
增删改查功能
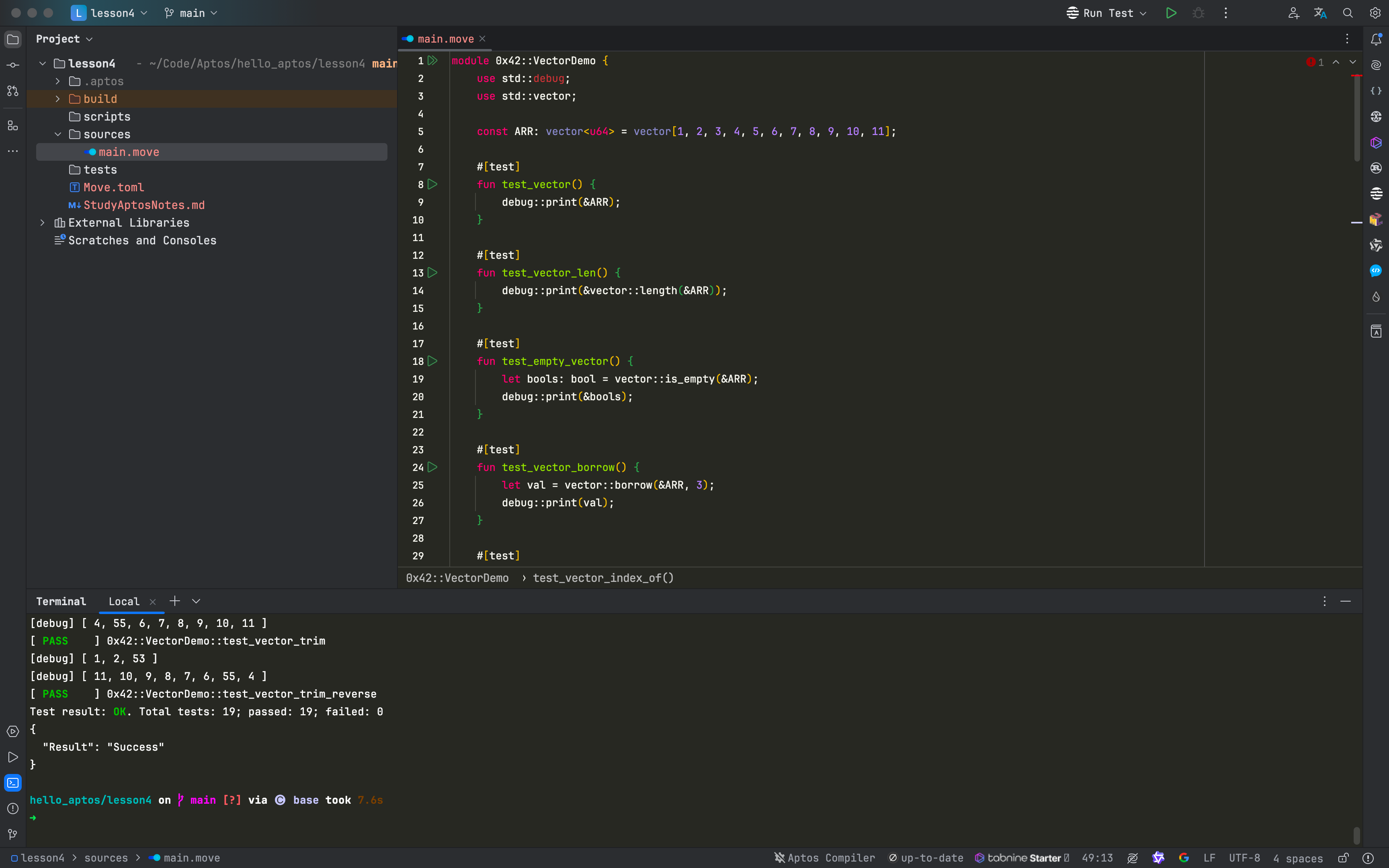
module 0x42::VectorDemo {
use std::debug;
use std::vector;
const ARR: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
#[test]
fun test_vector() {
debug::print(&ARR);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_len() {
debug::print(&vector::length(&ARR));
}
#[test]
fun test_empty_vector() {
let bools: bool = vector::is_empty(&ARR);
debug::print(&bools);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_borrow() {
let val = vector::borrow(&ARR, 3);
debug::print(val);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_borrow_mut() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
let val = vector::borrow_mut(&mut arr, 3);
debug::print(val);
*val = 100;
debug::print(val);
debug::print(&arr);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_contains() {
let n: u64 = 3;
let n2: u64 = 100;
debug::print(&vector::contains(&ARR, &n));
let bools: bool = vector::contains(&ARR, &n2);
debug::print(&bools);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_index_of() {
let n: u64 = 3;
let n2: u64 = 100;
let (isIndex, index) = vector::index_of(&ARR, &n);
let (isIndex2, index2) = vector::index_of(&ARR, &n2);
debug::print(&isIndex);
debug::print(&index);
debug::print(&isIndex2);
debug::print(&index2);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_push_back() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
vector::push_back(&mut arr, 100);
debug::print(&arr);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_append() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
let arr2: vector<u64> = vector[100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000,
1100];
vector::append(&mut arr, arr2);
debug::print(&arr);
}
#[test]
fun test_reverse_append() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
let arr2: vector<u64> = vector[100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000,
1100];
vector::reverse_append(&mut arr, arr2);
debug::print(&arr);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_pop_back() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
let val = vector::pop_back(&mut arr);
debug::print(&val);
debug::print(&arr);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_insert() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
vector::insert(&mut arr, 3, 100);
debug::print(&arr);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_remove() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
let val = vector::remove(&mut arr, 3);
debug::print(&val);
debug::print(&arr);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_swap() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
vector::swap(&mut arr, 3, 4);
debug::print(&arr);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_reverse() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 53, 4, 55, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
vector::reverse(&mut arr);
debug::print(&arr);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_rotate() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 53, 4, 55, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
vector::rotate(&mut arr, 3);
debug::print(&arr);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_swap_remove() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 53, 4, 55, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
let val = vector::swap_remove(&mut arr, 3);
debug::print(&val);
debug::print(&arr);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_trim() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 53, 4, 55, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
let arr2 = vector::trim(&mut arr, 3);
debug::print(&arr);
debug::print(&arr2);
}
#[test]
fun test_vector_trim_reverse() {
let arr: vector<u64> = vector[1, 2, 53, 4, 55, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11];
let arr2 = vector::trim_reverse(&mut arr, 3);
debug::print(&arr);
debug::print(&arr2);
}
}
测试
hello_aptos/lesson4 on main [?] via 🅒 base
➜ aptos move test
INCLUDING DEPENDENCY AptosFramework
INCLUDING DEPENDENCY AptosStdlib
INCLUDING DEPENDENCY MoveStdlib
BUILDING lesson4
warning: unused alias
┌─ /Users/qiaopengjun/Code/Aptos/hello_aptos/lesson4/sources/main.move:2:14
│
2 │ use std::debug;
│ ^^^^^ Unused 'use' of alias 'debug'. Consider removing it
warning: unused alias
┌─ /Users/qiaopengjun/Code/Aptos/hello_aptos/lesson4/sources/main.move:3:14
│
3 │ use std::vector;
│ ^^^^^^ Unused 'use' of alias 'vector'. Consider removing it
Running Move unit tests
[debug] false
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_empty_vector
[debug] [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 1100, 1000, 900, 800, 700, 600, 500, 400, 300, 200, 100 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_reverse_append
[debug] [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector
[debug] [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000, 1100 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_append
[debug] 4
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_borrow
[debug] 4
[debug] 100
[debug] [ 1, 2, 3, 100, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_borrow_mut
[debug] true
[debug] false
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_contains
[debug] true
[debug] 2
[debug] false
[debug] 0
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_index_of
[debug] [ 1, 2, 3, 100, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_insert
[debug] 11
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_len
[debug] 11
[debug] [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_pop_back
[debug] [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 100 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_push_back
[debug] 4
[debug] [ 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_remove
[debug] [ 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 55, 4, 53, 2, 1 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_reverse
[debug] [ 4, 55, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 1, 2, 53 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_rotate
[debug] [ 1, 2, 3, 5, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_swap
[debug] 4
[debug] [ 1, 2, 53, 11, 55, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_swap_remove
[debug] [ 1, 2, 53 ]
[debug] [ 4, 55, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_trim
[debug] [ 1, 2, 53 ]
[debug] [ 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 55, 4 ]
[ PASS ] 0x42::VectorDemo::test_vector_trim_reverse
Test result: OK. Total tests: 19; passed: 19; failed: 0
{
"Result": "Success"
}
hello_aptos/lesson4 on main [?] via 🅒 base took 7.6s
➜
总结
本文详细解读了 Aptos Move 语言中的 Vector 数据结构,介绍了其核心特性和常见的增删改查操作。通过多个代码示例,我们展示了如何高效地使用 Vector 进行数据管理,并结合单元测试验证了这些操作的正确性。Vector 作为智能合约中常用的数据结构,具有灵活性和高效性,掌握它的使用方法能够大大提升开发效率。希望通过本篇文章,读者可以对 Vector 的特性和应用有更深入的理解,在后续开发中灵活运用这一工具。
参考
点赞 0
收藏 0
分享
本文参与登链社区写作激励计划 ,好文好收益,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入。
0 条评论
请先 登录 后评论
