如何使用 Reth 构建自定义 RPC 方法
- QuickNode
- 发布于 2025-09-26 10:42
- 阅读 1237
本文介绍了如何使用 Reth 构建自定义 RPC 方法,以扩展标准的 Ethereum JSON-RPC API。通过创建一个名为 eth_getBlockUtilization 的 RPC 方法,可以检索当前或历史区块的利用率。文章详细说明了代码实现、项目设置、编译和运行自定义 RPC 方法的步骤,并提供了测试和验证方法。
概述
想过构建自己的自定义 Web3 API 吗?Reth 现在允许你使用自定义功能扩展标准的 Ethereum JSON-RPC API,而无需 fork 代码库。这开启了构建 Marketplace add-on 以用于 DeFi、专用索引器等的可能性。
本指南将引导你使用 Reth 构建和部署自定义 RPC 方法。具体来说,我们将创建一个名为 eth_getBlockUtilization 的 RPC 方法,该方法检索当前或历史区块利用率。
要了解更多关于如何构建自己的 Marketplace Add-on 的信息,请查看本指南
你将学到什么
- 了解 Reth
- 构建自定义 RPC 方法
- 使用自定义 RPC 方法配置运行你的 Reth 节点
- 测试和验证自定义 RPC 方法
你需要什么
- 一个正在运行的 Reth 节点 - 首先按照我们的 如何运行 Reth 节点 指南进行操作
- Rust 开发环境 (rustc 1.86+)
- 带有 WSL 的 Linux、macOS 或 Windows
- 安装 Git
- 基本熟悉 Rust 编程和 JSON-RPC 概念
- 了解 Ethereum 架构、交易和智能合约
什么是 Reth?
Reth 是用 Rust 编写的高性能 Ethereum 执行客户端。它被设计为模块化、快速且对开发者友好,同时保持与 Ethereum 的完全兼容。
Reth 上的自定义 RPC 方法
Reth 现在允许原生构建自定义 RPC 方法,而无需维护链更新,就像你在一个 fork 的代码库中可能做的那样。这意味着更少的调试和维护代码的时间。要使用自定义 RPC 方法,你需要启用 --extended-eth-namespace 标志来运行你的 Reth 节点。这意味着我们需要暂时停止我们的节点,以便使用所需的配置重新启动它。
让我们深入研究代码。
代码审查
本指南涵盖构建一个名为 eth_getBlockUtilization 的方法,该方法可以查询当前或历史区块的利用率。
此自定义方法的逻辑将位于 reth/src/main.rs 文件中。让我们逐一查看代码。
导入
//! Custom Reth client with extended ETH namespace for block utilization metrics
//![allow(unused_crate_dependencies)]
use clap::Parser;
use jsonrpsee::{core::RpcResult, proc_macros::rpc, types::ErrorObjectOwned};
use reth_ethereum::{
cli::{chainspec::EthereumChainSpecParser, interface::Cli},
node::EthereumNode,
};
use alloy_rpc_types::BlockNumberOrTag;
use reth_provider::{BlockReaderIdExt, HeaderProvider};
use reth_primitives::Header;
主函数 - fn main()
fn main() {
Cli::<EthereumChainSpecParser, RethCliExtended>::parse()
.run(|builder, args| async move {
let handle = builder
.node(EthereumNode::default())
.extend_rpc_modules(move |ctx| {
if !args.extended_eth_namespace {
return Ok(());
}
let provider = ctx.provider().clone();
let ext = BlockUtilizationImpl::new(provider);
ctx.modules.merge_configured(ext.into_rpc())?;
println!("Extended ETH namespace enabled with eth_getBlockUtilization");
Ok(())
})
.launch()
.await?;
handle.wait_for_node_exit().await
})
.unwrap();
}
发生了什么:
Cli::<EthereumChainSpecParser, RethCliExtended>::parse()- 使用类型来允许不同的链规范和 CLI 扩展builder.node(EthereumNode::default())- 设置基本的 Ethereum 节点实现extend_rpc_modules(move)|ctx| - 提供一个Hook来添加自定义 RPC 方法ctx.provider().clone()- 访问区块链数据提供程序ctx.modules.merge_configured(ext.into_rpc())?- 注册新的 RPC 方法
配置扩展
#[derive(Default, clap::Args)]
struct RethCliExtended {
#[arg(long)]
extended_eth_namespace: bool,
}
发生了什么:
#[derive(Default, clap::Args)]- 自动 CLI 参数解析#[arg(long)]- 创建 --enable-custom-rpc 命令行标志- 该结构扩展了 Reth 的基本 CLI,而无需修改核心代码
RPC 特征定义
//![cfg_attr(not(test), rpc(server, namespace = "eth"))]
//![cfg_attr(test, rpc(server, client, namespace = "eth"))]
/// RPC trait for block utilization methods
/// 用于区块利用率方法的 RPC trait
pub trait BlockUtilizationNamespace {
/// Returns the gas utilization percentage for a given block
/// 返回给定区块的 gas 利用率百分比
#[method(name = "getBlockUtilization")]
fn get_block_utilization(&self, block_number: BlockNumberOrTag) -> RpcResult<f64>;
}
发生了什么:
#[rpc(server, namespace = "eth")]- 宏生成 JSON-RPC 服务器样板namespace = "eth"- 创建方法 eth_getBlockUtilization (命名空间 + 方法名称)BlockNumberOrTag- 用于指定区块的标准 Ethereum 类型(latest、earliest、number)RpcResult<f64>- 用于返回利用率百分比的 RPC 响应的标准化错误处理
实现结构
/// Implementation of block utilization RPC methods
/// 区块利用率 RPC 方法的实现
//![derive(Debug)]
pub struct BlockUtilizationImpl<Provider> {
provider: Provider,
}
impl<Provider> BlockUtilizationImpl<Provider>
where
Provider: BlockReaderIdExt + HeaderProvider + Clone + Unpin + 'static,
{
/// Creates a new BlockUtilizationImpl instance
/// 创建一个新的 BlockUtilizationImpl 实例
pub fn new(provider: Provider) -> Self {
Self { provider }
}
}
发生了什么:
- 泛型
Provider类型允许数据源实现的灵活性 - 特征边界确保提供程序支持区块读取和 header 访问
- 用于异步 RPC 处理的
Clone+Unpin+static要求
核心逻辑实现
impl<Provider> BlockUtilizationNamespaceServer for BlockUtilizationImpl<Provider>
where
Provider: BlockReaderIdExt + HeaderProvider + Clone + Unpin + 'static,
Provider::Header: Into<Header> + Clone,
{
fn get_block_utilization(&self, block_number: BlockNumberOrTag) -> RpcResult<f64> {
// Convert BlockNumberOrTag to actual block number
// 将 BlockNumberOrTag 转换为实际区块号
let block_num = match block_number {
BlockNumberOrTag::Number(num) => num,
BlockNumberOrTag::Latest => {
match self.provider.best_block_number() {
Ok(num) => num,
Err(e) => return Err(ErrorObjectOwned::owned(
-32000,
format!("Failed to get latest block number: {}", e),
None::<()>,
)),
}
}
BlockNumberOrTag::Earliest => 0,
BlockNumberOrTag::Pending => {
return Err(ErrorObjectOwned::owned(
-32000,
"Pending block not supported for utilization calculation",
None::<()>,
));
}
_ => return Err(ErrorObjectOwned::owned(
-32000,
"Unsupported block number tag",
None::<()>,
)),
};
// Get the header using HeaderProvider
// 使用 HeaderProvider 获取 header
let header = match self.provider.header_by_number(block_num) {
Ok(Some(header)) => header,
Ok(None) => return Err(ErrorObjectOwned::owned(
-32000,
"Block header not found",
None::<()>,
)),
Err(e) => return Err(ErrorObjectOwned::owned(
-32000,
format!("Provider error: {}", e),
None::<()>,
)),
};
// Convert to Header type and access fields directly
// 转换为 Header 类型并直接访问字段
let header: Header = header.into();
let gas_limit = header.gas_limit;
let gas_used = header.gas_used;
if gas_limit == 0 {
return Ok(0.0);
}
let utilization = (gas_used as f64 / gas_limit as f64) * 100.0;
let utilization = (utilization * 100.0).round() / 100.0;
Ok(utilization)
}
}
发生了什么:
- 区块号解析处理不同的标签类型(latest、earliest、specific block number)
- Header 检索,对丢失的区块进行全面的错误处理
- 利用率计算:
(gas_used / gas_limit) * 100 - 结果四舍五入到小数点后 2 位,以实现一致的格式
- 对于 gas 限制为零的区块,返回 0.0(边缘情况处理)
现在我们对代码有了更好的理解,让我们进入项目设置。
前提条件检查
首先,为了进行健全性检查,我们将验证我们的环境,检查我们的节点是否正在运行以及它是否已同步。请注意,如果你的节点未在 localhost:8545 上运行,你可能需要更新 cURL 请求以指向不同的 PORT。
## Check Rust version (need 1.86+)
## 检查 Rust 版本(需要 1.86+)
rustc --version
## Check if you have a running Reth node
## 检查你是否有一个正在运行的 Reth 节点
systemctl status reth.service
## Verify your node is synced
## 验证你的节点已同步
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"eth_syncing","params":[],"id":1}' \
localhost:8545
在继续之前验证节点是否已同步,以确保我们可以获取最新的区块。
设置 Reth 项目
我们将修改现有的 Reth 安装以添加我们的自定义 RPC 方法。请注意,你可能需要根据需要在你的 PATH 中更新。
- 首先,导航到你的 Reth 目录:
cd /data/reth
重要提示:调整到你的 Reth 安装的路径
- 然后,备份你当前的 main.rs:
cp bin/reth/src/main.rs bin/reth/src/main.rs.backup
记得保存文件。
实现区块利用率 RPC 方法
现在让我们实现我们的自定义 RPC 方法,这些方法提供我们的区块利用率指标。
将 bin/reth/src/main.rs 的内容替换为此指南前面我们讨论过的以下代码:
use clap::Parser;
use jsonrpsee::{core::RpcResult, proc_macros::rpc, types::ErrorObjectOwned};
use reth_ethereum::{
cli::{chainspec::EthereumChainSpecParser, interface::Cli},
node::EthereumNode,
};
use alloy_rpc_types::BlockNumberOrTag;
use reth_provider::{BlockReaderIdExt, HeaderProvider};
use reth_primitives::Header;
fn main() {
Cli::<EthereumChainSpecParser, RethCliExtended>::parse()
.run(|builder, args| async move {
let handle = builder
.node(EthereumNode::default())
.extend_rpc_modules(move |ctx| {
if !args.extended_eth_namespace {
return Ok(());
}
let provider = ctx.provider().clone();
let ext = BlockUtilizationImpl::new(provider);
ctx.modules.merge_configured(ext.into_rpc())?;
println!("Extended ETH namespace enabled with eth_getBlockUtilization");
Ok(())
})
.launch()
.await?;
handle.wait_for_node_exit().await
})
.unwrap();
}
/// Custom CLI args extension that adds the extended namespace flag
/// 自定义 CLI 参数扩展,添加扩展的命名空间标志
//![derive(Debug, Clone, Copy, Default, clap::Args)]
struct RethCliExtended {
/// CLI flag to enable the extended ETH namespace
/// 用于启用扩展 ETH 命名空间的 CLI 标志
#[arg(long)]
pub extended_eth_namespace: bool,
}
/// RPC trait defining our block utilization methods
/// RPC trait 定义了我们的区块利用率方法
//![cfg_attr(not(test), rpc(server, namespace = "eth"))]
//![cfg_attr(test), rpc(server, client, namespace = "eth"))]
pub trait BlockUtilizationNamespace {
/// Get block utilization as percentage (gas_used / gas_limit * 100)
/// 获取区块利用率百分比 (gas_used / gas_limit * 100)
#[method(name = "getBlockUtilization")]
fn get_block_utilization(&self, block_number: BlockNumberOrTag) -> RpcResult<f64>;
}
/// Implementation struct that holds the blockchain data provider
/// 实现结构体,持有区块链数据提供程序
pub struct BlockUtilizationImpl<Provider> {
provider: Provider,
}
impl<Provider> BlockUtilizationImpl<Provider>
where
Provider: BlockReaderIdExt + HeaderProvider + Clone + Unpin + 'static,
Provider::Header: Into<Header> + Clone,
{
pub fn new(provider: Provider) -> Self {
Self { provider }
}
}
/// Implementation of our custom RPC methods
/// 我们自定义 RPC 方法的实现
impl<Provider> BlockUtilizationNamespaceServer for BlockUtilizationImpl<Provider>
where
Provider: BlockReaderIdExt + HeaderProvider + Clone + Unpin + 'static,
Provider::Header: Into<Header> + Clone,
{
fn get_block_utilization(&self, block_number: BlockNumberOrTag) -> RpcResult<f64> {
// Convert BlockNumberOrTag to actual block number
// 将 BlockNumberOrTag 转换为实际区块号
let block_num = match block_number {
BlockNumberOrTag::Number(num) => num,
BlockNumberOrTag::Latest => {
match self.provider.best_block_number() {
Ok(num) => num,
Err(e) => return Err(ErrorObjectOwned::owned(
-32000,
format!("Failed to get latest block number: {}", e),
None::<()>,
)),
}
}
BlockNumberOrTag::Earliest => 0,
BlockNumberOrTag::Pending => {
return Err(ErrorObjectOwned::owned(
-32000,
"Pending block not supported for utilization calculation",
None::<()>,
));
}
_ => return Err(ErrorObjectOwned::owned(
-32000,
"Unsupported block number tag",
None::<()>,
)),
};
// Get the block header using HeaderProvider
// 使用 HeaderProvider 获取区块 header
let header = match self.provider.header_by_number(block_num) {
Ok(Some(header)) => header,
Ok(None) => return Err(ErrorObjectOwned::owned(
-32000,
"Block header not found",
None::<()>,
)),
Err(e) => return Err(ErrorObjectOwned::owned(
-32000,
format!("Provider error: {}", e),
None::<()>,
)),
};
// Convert to Header type and access gas fields
// 转换为 Header 类型并访问 gas 字段
let header: Header = header.into();
let gas_limit = header.gas_limit;
let gas_used = header.gas_used;
if gas_limit == 0 {
return Ok(0.0);
}
let utilization = (gas_used as f64 / gas_limit as f64) * 100.0;
let utilization = (utilization * 100.0).round() / 100.0;
Ok(utilization)
}
}
记得保存文件。现在让我们继续编译代码。
构建自定义 RPC 方法
- 编译你的自定义 RPC 方法:
source ~/.cargo/env
cd /data/reth
cargo check --bin reth
如果遇到编译错误,请验证所有导入是否正确,并且依赖项是否在 Cargo.toml 中正确配置。
- 在发布模式下构建:
cargo build --release --bin reth
注意:初始构建可能需要 10-15 分钟,因为它使用你的自定义 RPC 方法编译整个 Reth 代码库。
运行自定义 RPC 方法
你的 Reth 节点需要启用 --extended-eth-namespace 命令行标志才能使用自定义 RPC 方法。这允许你使用或不使用扩展功能运行相同的二进制文件。
为此,请使用扩展的 eth-namespace 标志启动 Reth:
cd /path/to/reth
./target/release/reth node \
--chain <your-chain-name> \
--datadir /path/to/data/<your-chain-name> \
--http --http.addr 0.0.0.0 --http.port 8545 \
--authrpc.addr 127.0.0.1 --authrpc.port 8551 \
--authrpc.jwtsecret /path/to/jwtsecret \
--full \
--extended-eth-namespace
记住将 /path/to/ 更新为你的正确路径。
检查以确保你的节点没有遇到任何初始化错误,并继续与链顶端同步。
Systemd 服务配置
通常,你通过 Systemd 运行节点,因此你不需要始终使其在终端中运行。为此,让我们首先停止我们的节点,然后更新 ExecStart 命令以包括扩展的命名空间。
sudo systemctl stop reth.service
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/reth.service
可以在此处找到我们 Reth 服务的完整代码。
更新 ExecStart 行以包括扩展的命名空间标志:
ExecStart=/path/to/reth/target/release/reth node \
--chain <your-chain-name> \
--datadir /path/to/data/<your-chain-name> \
--http --http.addr 0.0.0.0 --http.port 8545 \
--authrpc.addr 127.0.0.1 --authrpc.port 8551 \
--authrpc.jwtsecret /path/to/jwtsecret \
--full \
--extended-eth-namespace
其中:
/path/to/reth:构建 Reth 二进制文件的文件夹<your-chain-name>:你的链(例如,hoodi)/path/to/data/...:节点数据的目录/path/to/jwtsecret:你的 JWT 密钥文件的路径
记得保存文件。
然后,重新启动服务:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start reth.service
sudo journalctl -u reth.service -f
现在我们的方法已添加,让我们对其进行测试!
测试你的自定义 RPC 方法
让我们验证我们的自定义 RPC 方法是否使用当前和历史区块数据正常工作。
- 使用最新区块进行测试:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"eth_getBlockUtilization","params":["latest"],"id":1}' \
localhost:8545
响应:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":66.45}
在我们测试时,这是区块 1247242。
- 使用特定区块进行测试(例如,1247240)
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"eth_getBlockUtilization","params":["0x130808"],"id":2}' \
localhost:8545
响应:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":3.34}
- 现在,让我们测试错误处理:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"eth_getBlockUtilization","params":["0x99999999"],"id":3}' \
localhost:8545
响应:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":3,"error":{"code":-32000,"message":"Block header not found"}}
为了给我们更多的安全感,让我们通过使用区块浏览器并手动调用 eth_getBlockByNumber 来交叉检查我们的结果来进行健全性检查。
让我们测试区块 117500。Etherscan 显示 98.61%:
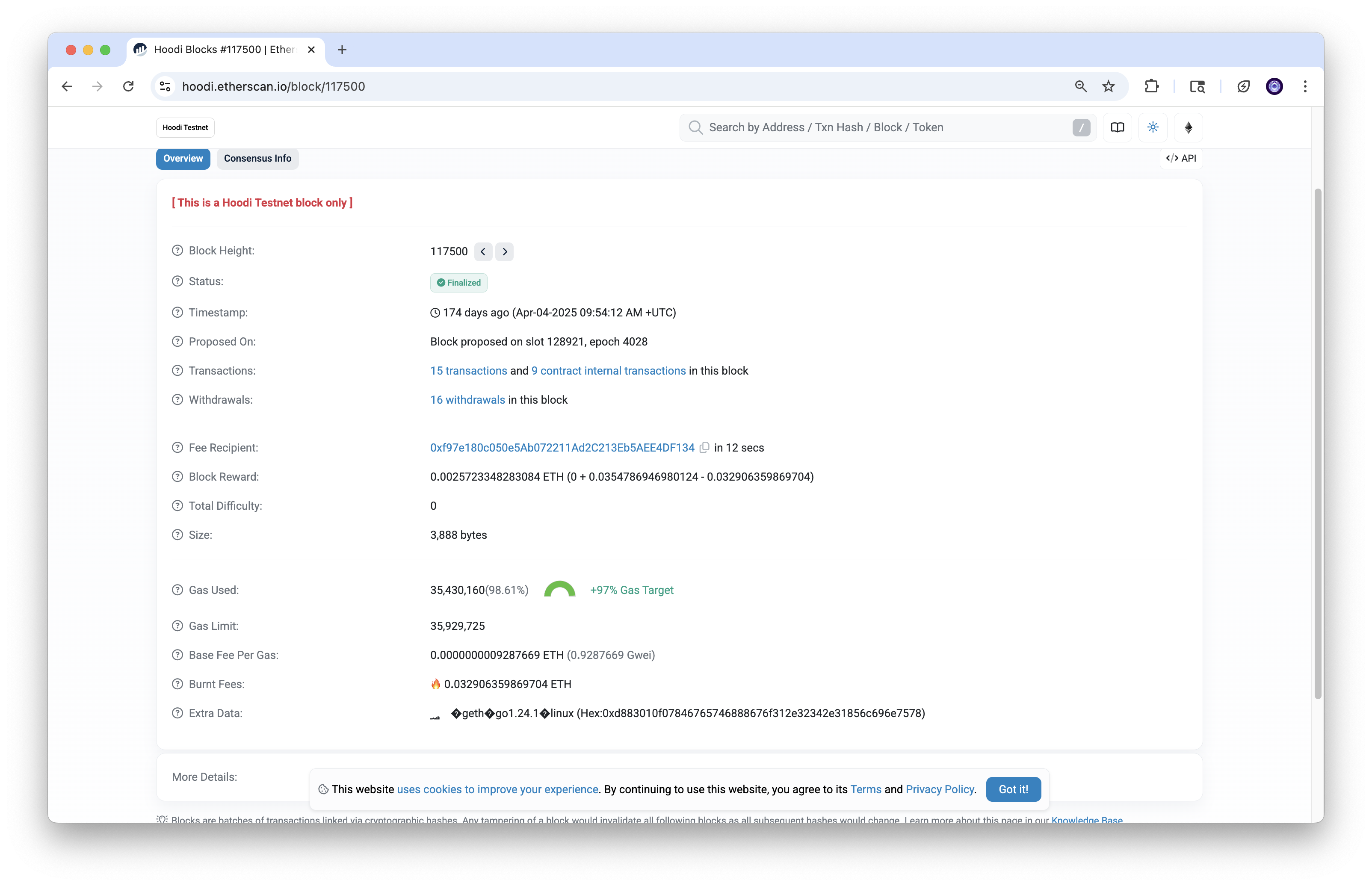
现在,让我们调用:
curl -s -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"eth_getBlockByNumber","params":["0x1cafc",false],"id":1}' \
http://127.0.0.1:8545
通过响应,我们可以通过从 gasUsed 和 gasLimit 中提取十六进制值,将它们转换为整数并将其相除来手动进行计算。
..."gasLimit":"0x2243e7d","gasUsed":"0x21c9f10"...
例如:
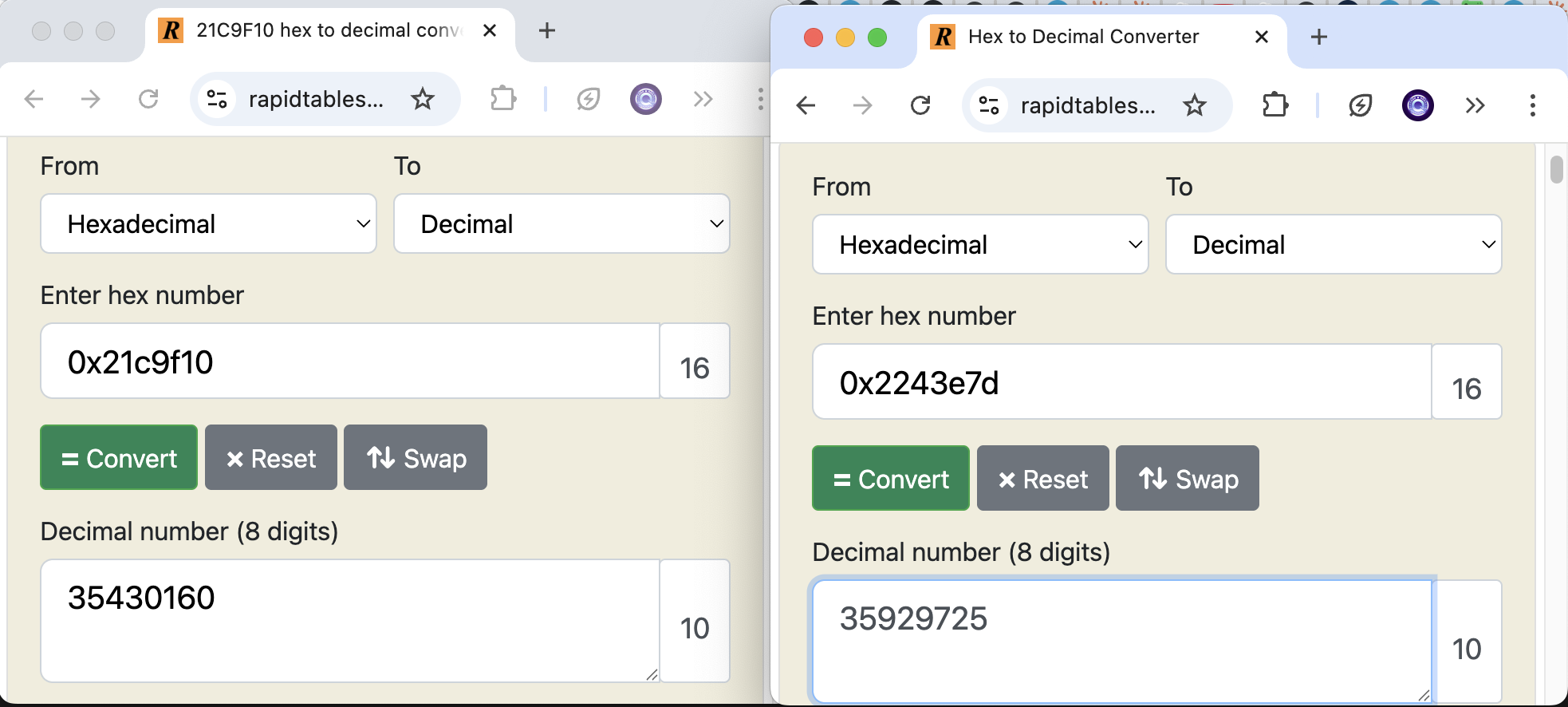
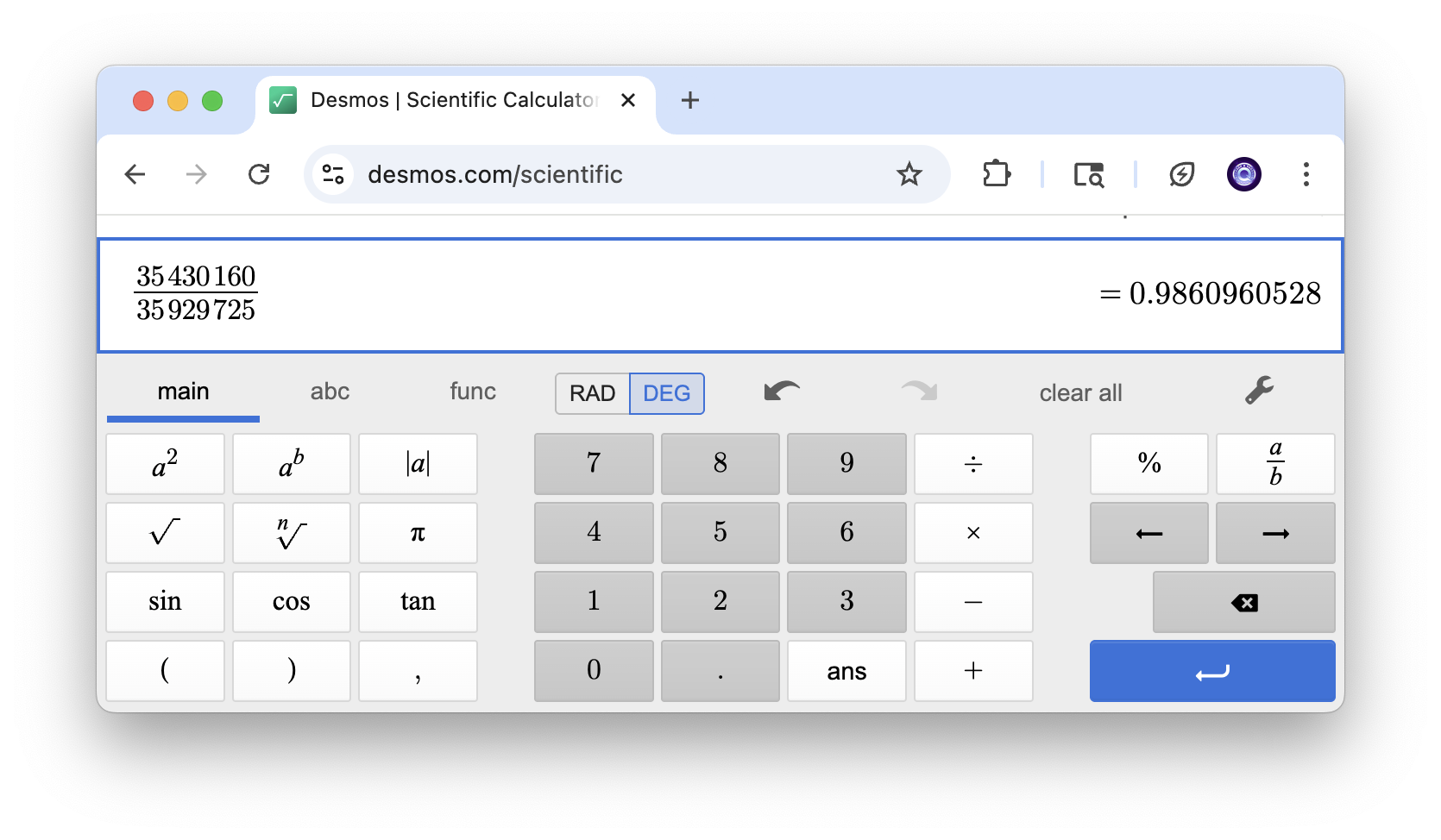
这证实了我们的自定义 eth_getBlockUtilization RPC 方法正常工作并提供准确的 gas 利用率百分比。
通过 QuickNode Marketplace 赚取收入
如果你看到构建有用的 RPC 方法的机会,你可以将其放在 QuickNode Marketplace 上并赚取收入。查看我们的技术指南 和课程来构建你自己的 Marketplace add-on。
你想要构建的自定义 RPC 方法可能已经创建!这意味着你可以减少开发和维护基础设施的时间。查看 QuickNode Marketplace 以查看 70 多个链上可用的 add-on 列表。
最后的想法
恭喜!你已成功学习如何在 Reth 中构建、部署和管理自定义 RPC 方法。这种强大的模式使你能够使用专门的功能扩展以太坊的 JSON-RPC API,而无需维护 fork 的代码库。通过尝试以下步骤,继续在你学到的知识的基础上构建:
- 探索对 DeFi 和 NFT 生态系统有用的想法,例如构建一种可以一次交换多个代币或 NFT 的 RPC 方法,检查多个 DEX 上的流动性,或者你当前使用的现有方法,但可以添加一些改进
- 加入 Reth Discord 社区进行高级讨论
- 将你的自定义 RPC 方法贡献回 Reth 生态系统
订阅我们的 QuickNode Newsletter 以获取更多关于以太坊基础设施的文章和指南。在 Twitter 上与我们联系或在我们的 Discord 社区中聊天!
我们的 ❤️ 反馈!
如果你对新主题有任何反馈或请求,请告诉我们。我们很乐意听取你的意见。
- 原文链接: quicknode.com/guides/inf...
- 登链社区 AI 助手,为大家转译优秀英文文章,如有翻译不通的地方,还请包涵~
- 以太坊:区块链的根本价值与应用 99 浏览
- 生产级的全同步可组合性现已上线 59 浏览
- 34 个资源:探索、构建和部署基于 ERC-8004 的信任最小化 AI 代理 205 浏览
- 以太坊:应用层开放思维,不弃核心原则 247 浏览
- 理解区块级访问列表 344 浏览
- 以太坊 2029 Strawmap 傻瓜指南 320 浏览
- 以太坊:构建去极权化的数字庇护所 349 浏览
- Orca Whirlpools 对比 Uniswap V3 — ImmuneBytes 226 浏览
- 十年账户抽象,终获解决 270 浏览
- Vitalik: 以太坊量子抵抗路线图 300 浏览
- 失效的 Groth16 `delta == gamma == G2 生成元` 358 浏览
- 介绍 strawmap,一份由 EF 协议推出的概念路线图 416 浏览

