应用 ZK 解数独,无需泄露答案
- asecuritysite
- 发布于 2025-08-11 08:19
- 阅读 1890
本文介绍了如何使用zkSnark和ZoKrates工具包在以太坊上创建一个智能合约来解决数独问题,同时不泄露答案。文章详细展示了如何定义公共变量和私有变量,以及如何使用Zokrates插件在Remix中编写代码,生成零知识证明,并将验证密钥部署到智能合约中。
解数独——不泄露你的答案
我越是研究零知识证明(ZKP),就越觉得它们是解决更注重隐私的世界的方案——它们真是太棒了!
通过 zkSnark——一种非交互式的知识自适应论证——我们提供了一个从证明者到多个验证者的简短证明,证明我们拥有关于某些私有数据和函数(f)的特定知识。 证明速度很快。 因此,zkSnark 可以集成到以太坊中,我们可以在不实际泄露数据的情况下证明某些事情(例如私钥的所有权)。 其中一个最好的集成是 ZoKrates [这里],它是一个构建智能合约的工具包,可以隐藏私有数据[1][ 这里]:

现在,假设我们有一个数独谜题:
X X 3 X
2 X X 3
3 X X X
X 1 3 X我们现在可以创建一个解决方案的智能合约,但不泄露我们的答案吗? 好了,解决方案是:
1 3 2 4
2 4 1 3
3 2 4 1
4 1 3 2我们现在可以用以下方式定义单元格:
| a11 | a12 | [b11] | b12 |
--------------------------
| [a21] | a22 | b21 | [b22] |
--------------------------
| [c11] | c12 | d11 | d12 |
--------------------------
| c21 | [c22] | [d21] | d22 |在证明中,我们可以定义公共变量:
field a21, field b11, field b22, field c11, field c22, field d21这些将是在智能合约中显示的变量。 然后私钥可以是:
private field a11, private field a12, private field a22, private field b12, private field b21, private field c12, private field c21, private field d11, private field d12, private field d22首先,我们需要在 Remix 中安装 Zokrates 插件,现在可以输入我们的代码:
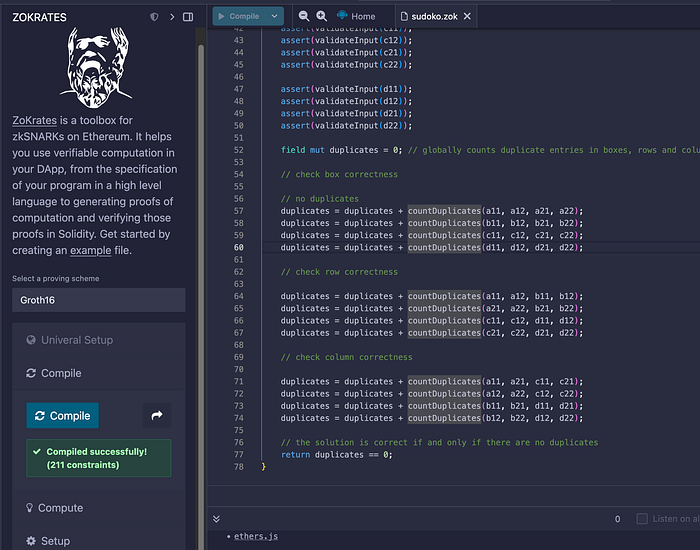
此处的代码为:
// Sudoku 的格式如下
// | a11 | a12 || b11 | b12 |
// --------------------------
// | a21 | a22 || b21 | b22 |
// ==========================
// | c11 | c12 || d11 | d12 |
// --------------------------
// | c21 | c22 || d21 | d22 |
// 我们使用 `[1, 2, 3, 4]` 作为值的简单编码,并依靠 if-else 语句来检测重复项
def countDuplicates(field e11, field e12, field e21, field e22) -> field {
field mut duplicates = e11 == e12 ? 1 : 0;
duplicates = duplicates + (e11 == e21 ? 1 : 0);
duplicates = duplicates + (e11 == e22 ? 1 : 0);
duplicates = duplicates + (e12 == e21 ? 1 : 0);
duplicates = duplicates + (e12 == e22 ? 1 : 0);
duplicates = duplicates + (e21 == e22 ? 1 : 0);
return duplicates;
}
// 如果 x 在 (1..4) 范围内,则返回 0
def validateInput(field x) -> bool {
return (x - 1) * (x - 2) * (x - 3) * (x - 4) == 0;
}
// 变量命名:box'行''列'
def main(field a21, field b11, field b22, field c11, field c22, field d21, private field a11, private field a12, private field a22, private field b12, private field b21, private field c12, private field c21, private field d11, private field d12, private field d22) -> bool {
// 验证输入
assert(validateInput(a11));
assert(validateInput(a12));
assert(validateInput(a21));
assert(validateInput(a22));
assert(validateInput(b11));
assert(validateInput(b12));
assert(validateInput(b21));
assert(validateInput(b22));
assert(validateInput(c11));
assert(validateInput(c12));
assert(validateInput(c21));
assert(validateInput(c22));
assert(validateInput(d11));
assert(validateInput(d12));
assert(validateInput(d21));
assert(validateInput(d22));
field mut duplicates = 0; // 全局统计框、行和列中的重复条目
// 检查框的正确性
// 没有重复项
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(a11, a12, a21, a22);
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(b11, b12, b21, b22);
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(c11, c12, c21, c22);
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(d11, d12, d21, d22);
// 检查行的正确性
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(a11, a12, b11, b12);
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(a21, a22, b21, b22);
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(c11, c12, d11, d12);
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(c21, c22, d21, d22);
// 检查列的正确性
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(a11, a21, c11, c21);
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(a12, a22, c12, c22);
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(b11, b21, d11, d21);
duplicates = duplicates + countDuplicates(b12, b22, d12, d22);
// 当且仅当没有重复项时,解决方案才是正确的
return duplicates == 0;
}我们现在可以查看 ABI:
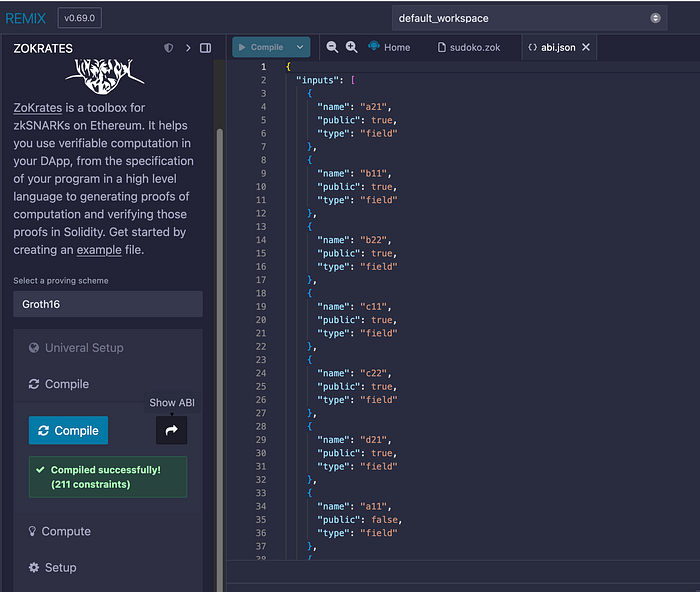
ABI 为:
{
"inputs": [\
{\
"name": "a21",\
"public": true,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "b11",\
"public": true,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "b22",\
"public": true,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "c11",\
"public": true,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "c22",\
"public": true,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "d21",\
"public": true,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "a11",\
"public": false,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "a12",\
"public": false,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "a22",\
"public": false,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "b12",\
"public": false,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "b21",\
"public": false,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "c12",\
"public": false,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "c21",\
"public": false,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "d11",\
"public": false,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "d12",\
"public": false,\
"type": "field"\
},\
{\
"name": "d22",\
"public": false,\
"type": "field"\
}\
],
"output": {
"type": "bool"
}
}然后我们可以输入我们的数据:
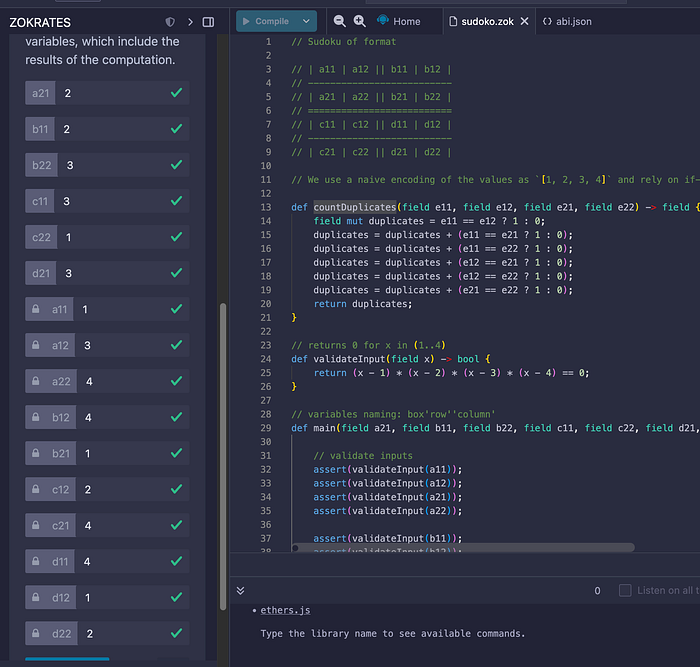
你可以看到输入值旁边有挂锁符号,表示它们是私有的。 然后我们可以检查我们的零知识证明并生成一个 witness:
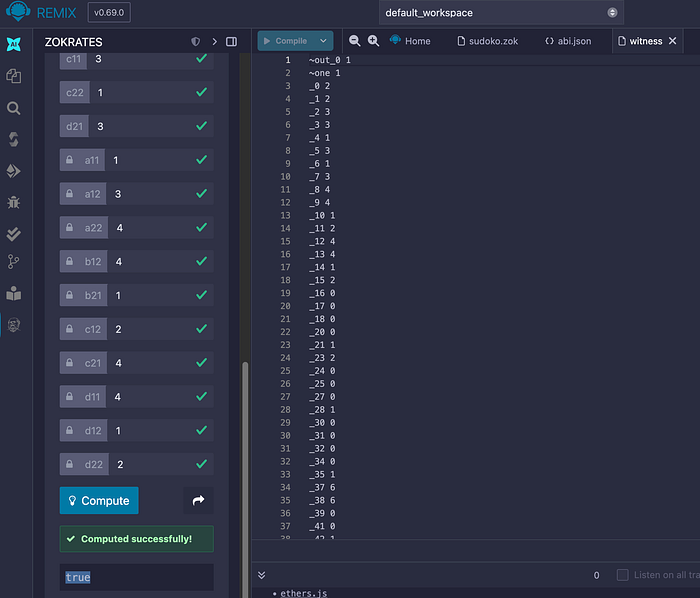
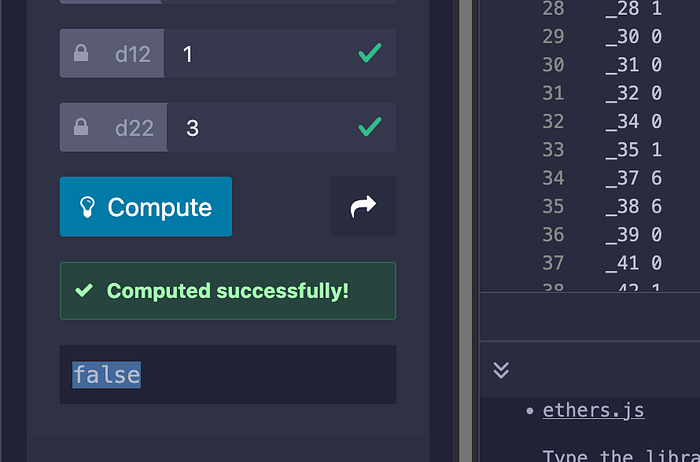
如果我们将 d22 的值更改为不正确的值,我们会从智能合约中得到一个 false 返回值:
然后我们可以使用以下命令创建验证密钥:
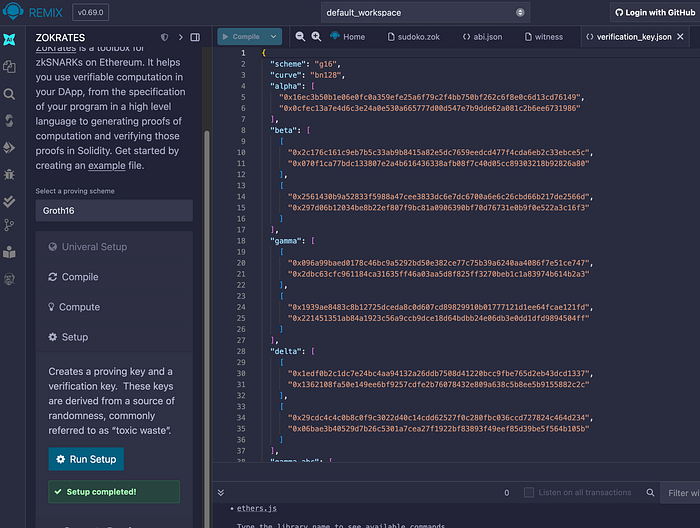
即:
{
"scheme": "g16",
"curve": "bn128",
"alpha": [\
"0x16ec3b50b1e06e0fc0a359efe25a6f79c2f4bb750bf262c6f8e0c6d13cd76149",\
"0x0cfec13a7e4d6c3e24a0e530a665777d00d547e7b9dde62a081c2b6ee6731986"\
],
"beta": [\
[\
"0x2c176c161c9eb7b5c33ab9b8415a82e5dc7659eedcd477f4cda6eb2c33ebce5c",\
"0x070f1ca77bdc133807e2a4b616436338afb08f7c40d05cc89303218b92826a80"\
],\
[\
"0x2561430b9a52833f5988a47cee3833dc6e7dc6700a6e6c26cbd66b217de2566d",\
"0x297d06b12034be8b22ef807f9bc81a0906390bf70d76731e0b9f0e522a3c16f3"\
]\
],
"gamma": [\
[\
"0x096a99baed0178c46bc9a5292bd50e382ce77c75b39a6240aa4086f7e51ce747",\
"0x2dbc63cfc961184ca31635ff46a03aa5d8f825ff3270beb1c1a83974b614b2a3"\
],\
[\
"0x1939ae8483c8b12725dceda8c0d607cd89829910b01777121d1ee64fcae121fd",\
"0x221451351ab84a1923c56a9ccb9dce18d64bdbb24e06db3e0dd1dfd9894504ff"\
]\
],
"delta": [\
[\
"0x1edf0b2c1dc7e24bc4aa94132a26ddb7508d41220bcc9fbe765d2eb43dcd1337",\
"0x1362108fa50e149ee6bf9257cdfe2b76078432e809a638c5b8ee5b9155882c2c"\
],\
[\
"0x29cdc4c4c0b8c0f9c3022d40c14cdd62527f0c280fbc036ccd727824c464d234",\
"0x06bae3b40529d7b26c5301a7cea27f1922bf83893f49eef85d39be5f564b105b"\
]\
],
"gamma_abc": [\
[\
"0x026a29883ebff51af882137e4b89da5acf6b3209d4db8423e124aee8c713c816",\
"0x2f5182150d62d7cb2962108384ee89a16f291e1df99ebfb6717e6e96550e3b3c"\
],\
[\
"0x2fb7488b3254541e1cb2f1cde2d284dd506d2533767bf73054da8a3efb75f57f",\
"0x1c74d32e6f77fdac92b4911351fabe477e69060d5e25e1977618c4d7468f9909"\
],\
[\
"0x01d5129aca2cacdbb5eb6fec3911785a6a099d2bef91625f91bfcf4b4515c840",\
"0x1812ccee72d7b894f6ccd48a3ff64a6d972cb8a45d5de8d5e5a3b243462c0776"\
],\
[\
"0x012b17ddd6d6aeabe6827cdd22382148777f5d7324c59f7a9c7a25f7395e71c7",\
"0x28fb621898aa465331d3ad4fdf1dfafffd2576fd02129c334131fe9ba25139c7"\
],\
[\
"0x199fe085d03195adb6ff0fb8282e5a6b29c08f0b9345f13e06361036a2eb4dbf",\
"0x07c34d3986e3bbe26ff360156bafcd3e8147330428bd85c411a17b9eef99b3b1"\
],\
[\
"0x1646e12f458a9a3c7396639ae1fab82e617370da21cd3b114c9a83834a46982a",\
"0x2b16c65462ab9bacc938290eb831fbfe140fcef7918ee3a7e4f25d2b45f835df"\
],\
[\
"0x0a5fc6a2a9f9886ef2d39a21ae8f9eb6407edc6fd3dde518815d474f5f1717c7",\
"0x15391f3a84fa4469a2f7d265c3333859082c69471306968a28a4105f0e2df424"\
],\
[\
"0x296ee1827f47e870ede6c2ed33ab18a903b6cea25b08a4bc1ee3367759a79013",\
"0x2e9bd4c62211542cf584b850d089db45afabda5a77e00d6feae3510381418c08"\
]\
]
}最后,我们可以创建一个证明:
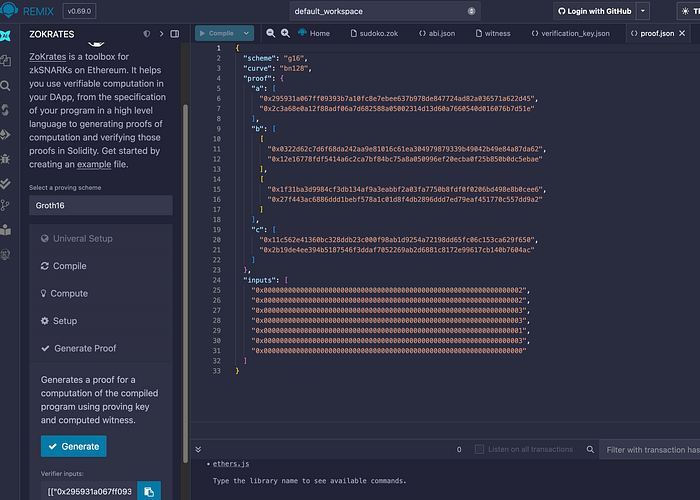
这将生成:
{
"scheme": "g16",
"curve": "bn128",
"proof": {
"a": [\
"0x295931a067ff09393b7a10fc8e7ebee637b978de847724ad82a036571a622d45",\
"0x2c3a68e0a12f88adf06a7d682588a05002314d13d60a7660540d016076b7d51e"\
],
"b": [\
[\
"0x0322d62c7d6f68da242aa9e81016c61ea304979879339b49042b49e84a87da62",\
"0x12e16778fdf5414a6c2ca7bf84bc75a8a050996ef20ecba0f25b850b0dc5ebae"\
],\
[\
"0x1f31ba3d9984cf3db134af9a3eabbf2a03fa7750b8fdf0f0206bd498e8b0cee6",\
"0x27f443ac6886ddd1bebf578a1c01d8f4db2896ddd7ed79eaf451770c557dd9a2"\
]\
],
"c": [\
"0x11c562e41360bc328ddb23c000f98ab1d9254a72198dd65fc06c153ca629f650",\
"0x2b19de4ee394b5187546f3ddaf7052269ab2d6881c8172e99617cb140b7604ac"\
]
},
"inputs": [\
"0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002",\
"0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002",\
"0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003",\
"0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003",\
"0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001",\
"0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003",\
"0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000"\
]
}最后,我们生成一个带有零知识证明的可部署智能合约:
// 此文件已获得 MIT 许可。
//
// 版权所有 2017 Christian Reitwiessner
// 特此授予任何获得本软件和相关文档文件(“软件”)副本的人免费许可,以处理本软件,不受限制,包括但不限于使用、复制、修改、合并、发布、分发、再许可和/或销售本软件副本的权利,并允许向其提供本软件的人员这样做,但须满足以下条件:
// 上述版权声明和本许可声明应包含在所有副本或本软件的实质部分中。
// 本软件按“原样”提供,不提供任何形式的明示或暗示的保证,包括但不限于适销性、特定用途的适用性和不侵权的保证。 在任何情况下,作者或版权所有者均不对任何索赔、损害或其他责任负责,无论是在合同诉讼、侵权诉讼或其他诉讼中,因本软件或本软件的使用或其他交易而产生或与之相关的责任。
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
library Pairing {
struct G1Point {
uint X;
uint Y;
}
// 字段元素的编码为:X[0] * z + X[1]
struct G2Point {
uint[2] X;
uint[2] Y;
}
/// @return G1 的生成器
function P1() pure internal returns (G1Point memory) {
return G1Point(1, 2);
}
/// @return G2 的生成器
function P2() pure internal returns (G2Point memory) {
return G2Point(
[10857046999023057135944570762232829481370756359578518086990519993285655852781,\
11559732032986387107991004021392285783925812861821192530917403151452391805634],
[8495653923123431417604973247489272438418190587263600148770280649306958101930,\
4082367875863433681332203403145435568316851327593401208105741076214120093531]
);
}
/// @return p 的否定,即 p.addition(p.negate()) 应该为零。
function negate(G1Point memory p) pure internal returns (G1Point memory) {
// G1 的基本字段 F_q 中的素数 q
uint q = 21888242871839275222246405745257275088696311157297823662689037894645226208583;
if (p.X == 0 && p.Y == 0)
return G1Point(0, 0);
return G1Point(p.X, q - (p.Y % q));
}
/// @return r,即 G1 上两点的和
function addition(G1Point memory p1, G1Point memory p2) internal view returns (G1Point memory r) {
uint[4] memory input;
input[0] = p1.X;
input[1] = p1.Y;
input[2] = p2.X;
input[3] = p2.Y;
bool success;
assembly {
success := staticcall(sub(gas(), 2000), 6, input, 0xc0, r, 0x60)
// 使用“invalid”使 gas 估算起作用
switch success case 0 { invalid() }
}
require(success);
}
/// @return r,即 G1 上的点与标量的乘积,即
/// 对于所有点 p,p == p.scalar_mul(1) 且 p.addition(p) == p.scalar_mul(2)。
function scalar_mul(G1Point memory p, uint s) internal view returns (G1Point memory r) {
uint[3] memory input;
input[0] = p.X;
input[1] = p.Y;
input[2] = s;
bool success;
assembly {
success := staticcall(sub(gas(), 2000), 7, input, 0x80, r, 0x60)
// 使用“invalid”使 gas 估算起作用
switch success case 0 { invalid() }
}
require (success);
}
/// @return 计算配对检查的结果
/// e(p1[0], p2[0]) * .... * e(p1[n], p2[n]) == 1
/// 例如,pairing([P1(), P1().negate()], [P2(), P2()]) 应该
/// 返回 true。
function pairing(G1Point[] memory p1, G2Point[] memory p2) internal view returns (bool) {
require(p1.length == p2.length);
uint elements = p1.length;
uint inputSize = elements * 6;
uint[] memory input = new uint[](inputSize);
for (uint i = 0; i < elements; i++)
{
input[i * 6 + 0] = p1[i].X;
input[i * 6 + 1] = p1[i].Y;
input[i * 6 + 2] = p2[i].X[1];
input[i * 6 + 3] = p2[i].X[0];
input[i * 6 + 4] = p2[i].Y[1];
input[i * 6 + 5] = p2[i].Y[0];
}
uint[1] memory out;
bool success;
assembly {
success := staticcall(sub(gas(), 2000), 8, add(input, 0x20), mul(inputSize, 0x20), out, 0x20)
// 使用“invalid”使 gas 估算起作用
switch success case 0 { invalid() }
}
require(success);
return out[0] != 0;
}
/// 方便的方法,用于检查两个对的配对。
function pairingProd2(G1Point memory a1, G2Point memory a2, G1Point memory b1, G2Point memory b2) internal view returns (bool) {
G1Point[] memory p1 = new G1Point[](2);
G2Point[] memory p2 = new G2Point[](2);
p1[0] = a1;
p1[1] = b1;
p2[0] = a2;
p2[1] = b2;
return pairing(p1, p2);
}
/// 方便的方法,用于检查三个对的配对。
function pairingProd3(
G1Point memory a1, G2Point memory a2,
G1Point memory b1, G2Point memory b2,
G1Point memory c1, G2Point memory c2
) internal view returns (bool) {
G1Point[] memory p1 = new G1Point[](3);
G2Point[] memory p2 = new G2Point[](3);
p1[0] = a1;
p1[1] = b1;
p1[2] = c1;
p2[0] = a2;
p2[1] = b2;
p2[2] = c2;
return pairing(p1, p2);
}
/// 方便的方法,用于检查四个对的配对。
function pairingProd4(
G1Point memory a1, G2Point memory a2,
G1Point memory b1, G2Point memory b2,
G1Point memory c1, G2Point memory c2,
G1Point memory d1, G2Point memory d2
) internal view returns (bool) {
G1Point[] memory p1 = new G1Point[](4);
G2Point[] memory p2 = new G2Point[](4);
p1[0] = a1;
p1[1] = b1;
p1[2] = c1;
p1[3] = d1;
p2[0] = a2;
p2[1] = b2;
p2[2] = c2;
p2[3] = d2;
return pairing(p1, p2);
}
}
``````markdown
contract Verifier {
using Pairing for *;
struct VerifyingKey {
Pairing.G1Point alpha;
Pairing.G2Point beta;
Pairing.G2Point gamma;
Pairing.G2Point delta;
Pairing.G1Point[] gamma_abc;
}
struct Proof {
Pairing.G1Point a;
Pairing.G2Point b;
Pairing.G1Point c;
}
function verifyingKey() pure internal returns (VerifyingKey memory vk) {
vk.alpha = Pairing.G1Point(uint256(0x16ec3b50b1e06e0fc0a359efe25a6f79c2f4bb750bf262c6f8e0c6d13cd76149), uint256(0x0cfec13a7e4d6c3e24a0e530a665777d00d547e7b9dde62a081c2b6ee6731986));
vk.beta = Pairing.G2Point([uint256(0x2c176c161c9eb7b5c33ab9b8415a82e5dc7659eedcd477f4cda6eb2c33ebce5c), uint256(0x070f1ca77bdc133807e2a4b616436338afb08f7c40d05cc89303218b92826a80)], [uint256(0x2561430b9a52833f5988a47cee3833dc6e7dc6700a6e6c26cbd66b217de2566d), uint256(0x297d06b12034be8b22ef807f9bc81a0906390bf70d76731e0b9f0e522a3c16f3)]);
vk.gamma = Pairing.G2Point([uint256(0x096a99baed0178c46bc9a5292bd50e382ce77c75b39a6240aa4086f7e51ce747), uint256(0x2dbc63cfc961184ca31635ff46a03aa5d8f825ff3270beb1c1a83974b614b2a3)], [uint256(0x1939ae8483c8b12725dceda8c0d607cd89829910b01777121d1ee64fcae121fd), uint256(0x221451351ab84a1923c56a9ccb9dce18d64bdbb24e06db3e0dd1dfd9894504ff)]);
vk.delta = Pairing.G2Point([uint256(0x1edf0b2c1dc7e24bc4aa94132a26ddb7508d41220bcc9fbe765d2eb43dcd1337), uint256(0x1362108fa50e149ee6bf9257cdfe2b76078432e809a638c5b8ee5b9155882c2c)], [uint256(0x29cdc4c4c0b8c0f9c3022d40c14cdd62527f0c280fbc036ccd727824c464d234), uint256(0x06bae3b40529d7b26c5301a7cea27f1922bf83893f49eef85d39be5f564b105b)]);
vk.gamma_abc = new Pairing.G1Point[](8);
vk.gamma_abc[0] = Pairing.G1Point(uint256(0x026a29883ebff51af882137e4b89da5acf6b3209d4db8423e124aee8c713c816), uint256(0x2f5182150d62d7cb2962108384ee89a16f291e1df99ebfb6717e6e96550e3b3c));
vk.gamma_abc[1] = Pairing.G1Point(uint256(0x2fb7488b3254541e1cb2f1cde2d284dd506d2533767bf73054da8a3efb75f57f), uint256(0x1c74d32e6f77fdac92b4911351fabe477e69060d5e25e1977618c4d7468f9909));
vk.gamma_abc[2] = Pairing.G1Point(uint256(0x01d5129aca2cacdbb5eb6fec3911785a6a099d2bef91625f91bfcf4b4515c840), uint256(0x1812ccee72d7b894f6ccd48a3ff64a6d972cb8a45d5de8d5e5a3b243462c0776));
vk.gamma_abc[3] = Pairing.G1Point(uint256(0x012b17ddd6d6aeabe6827cdd22382148777f5d7324c59f7a9c7a25f7395e71c7), uint256(0x28fb621898aa465331d3ad4fdf1dfafffd2576fd02129c334131fe9ba25139c7));
vk.gamma_abc[4] = Pairing.G1Point(uint256(0x199fe085d03195adb6ff0fb8282e5a6b29c08f0b9345f13e06361036a2eb4dbf), uint256(0x07c34d3986e3bbe26ff360156bafcd3e8147330428bd85c411a17b9eef99b3b1));
vk.gamma_abc[5] = Pairing.G1Point(uint256(0x1646e12f458a9a3c7396639ae1fab82e617370da21cd3b114c9a83834a46982a), uint256(0x2b16c65462ab9bacc938290eb831fbfe140fcef7918ee3a7e4f25d2b45f835df));
vk.gamma_abc[6] = Pairing.G1Point(uint256(0x0a5fc6a2a9f9886ef2d39a21ae8f9eb6407edc6fd3dde518815d474f5f1717c7), uint256(0x15391f3a84fa4469a2f7d265c3333859082c69471306968a28a4105f0e2df424));
vk.gamma_abc[7] = Pairing.G1Point(uint256(0x296ee1827f47e870ede6c2ed33ab18a903b6cea25b08a4bc1ee3367759a79013), uint256(0x2e9bd4c62211542cf584b850d089db45afabda5a77e00d6feae3510381418c08));
}
function verify(uint[] memory input, Proof memory proof) internal view returns (uint) {
uint256 snark_scalar_field = 21888242871839275222246405745257275088548364400416034343698204186575808495617;
VerifyingKey memory vk = verifyingKey();
require(input.length + 1 == vk.gamma_abc.length);
// Compute the linear combination vk_x
// 计算线性组合 vk_x
Pairing.G1Point memory vk_x = Pairing.G1Point(0, 0);
for (uint i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
require(input[i] < snark_scalar_field);
vk_x = Pairing.addition(vk_x, Pairing.scalar_mul(vk.gamma_abc[i + 1], input[i]));
}
vk_x = Pairing.addition(vk_x, vk.gamma_abc[0]);
if(!Pairing.pairingProd4(
proof.a, proof.b,
Pairing.negate(vk_x), vk.gamma,
Pairing.negate(proof.c), vk.delta,
Pairing.negate(vk.alpha), vk.beta)) return 1;
return 0;
}
function verifyTx(
Proof memory proof, uint[7] memory input
) public view returns (bool r) {
uint[] memory inputValues = new uint[](7);
for(uint i = 0; i < input.length; i++){
inputValues[i] = input[i];
}
if (verify(inputValues, proof) == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}这是一个完整部署的例子:
ZKPs Made Easy: zkWeb and ZoKrates
References
[1] Eberhardt, J., & Tai, S. (2018, July). Zokrates-scalable privacy-preserving off-chain computations. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData) (pp. 1084–1091). IEEE.
- 原文链接: medium.com/asecuritysite...
- 登链社区 AI 助手,为大家转译优秀英文文章,如有翻译不通的地方,还请包涵~
- 链下CLOB + 链上结算:构建高性能去中心化预测市场的完整技术栈 44 浏览
- Solidity动态数组全攻略:从零到精通,带你窥探EVM底层! 43 浏览
- 手把手教你玩转Solidity动态数组 43 浏览
- 《介绍 rwa [un]wind》 108 浏览
- 推出 ERC-8183:AI 智能体的商业层 144 浏览
- 深度拆解 Web3 预测市场:基于 Solidity 0.8.24 与 UMA 乐观预言机的核心实现 151 浏览
- 民主事物的再思考:构建共识发现工具 137 浏览
- Uniswap v3 白皮书与代码解析 160 浏览
- Zero 链: 技术定位报告 207 浏览
- 使用 OpenZeppelin 开发安全的智能合约 244 浏览
- 以太坊亟需的两大深度改造——二进制树 + VM 改造 243 浏览
- 使用OpenZeppelin Contracts设置Solidity智能合约项目 189 浏览

