zkMIPS解读
【zkMIPS系列】Poseidon hash设计流程 & 代码
- ZKM
- 发布于 2024-11-05 15:53
- 阅读 3109
Poseidon哈希函数原理
- 海绵结构
- 轮函数(常量加、非线性变换、线性变换) 2.1 Full Rounds变换 2.2 Partial Rounds变换 2.3 Permutation全流程
- Poseidon的吸入、置换、压缩
- Goldilocks域 & Plonky2中Poseidon的优化 4.1 Poseidon的MDS运行过程 4.2 Poseidon在Goldilocks域上的运行过程
1. 海绵结构
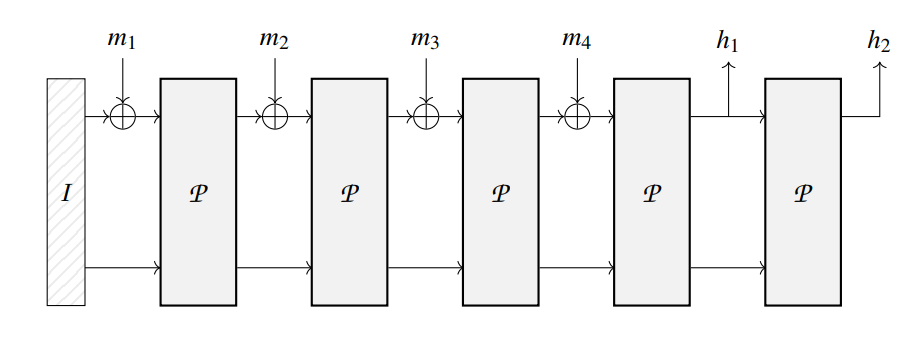
Poseidon哈希函数采用下面的海绵结构(Sponge Construction)来进行设计,其中P是Posedion每轮的置换函数,$I$是初始状态。假设初始状为$I$为全$0$向量,有一个消息$m=m_1||m_2||m_3||m_4$,输出为$h=h_1||h_2$,且每个$m_i$和$h_i$都是$r$位长度的,那么他们将经过以下模式来进行计算:
- $I$首先被赋值为$m_1$,并经过置换$P$,得到第一轮的长度为$r$的输出结果,随后和$m_2$进行异或,得到下一轮结果;
- 循环往复,直到输入$m_4$,随后输出前$r$位结果$h_1$,并将$h_1$再经过一次置换,得到结果$h_2$;
- 将$h=h_1||h_2$作为Poseidon hash的输出。
2. 轮函数(常量加、非线性变换、线性变换)
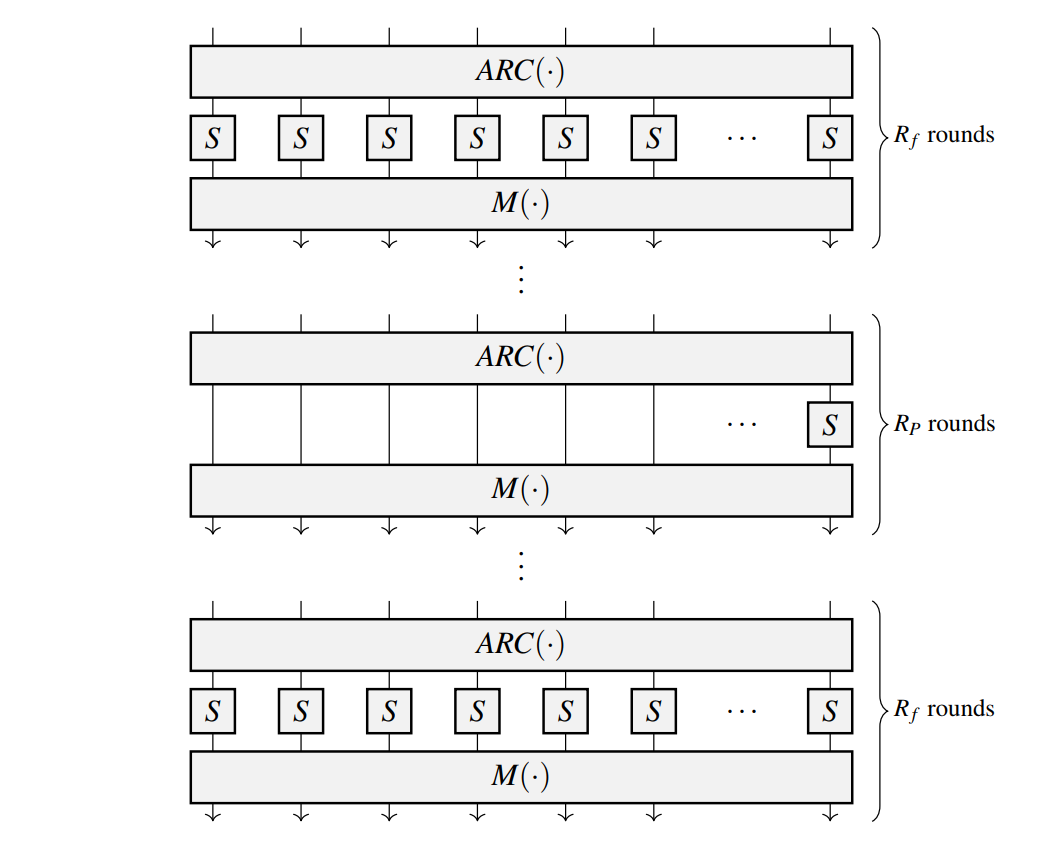
下图是Poseidon哈希函数对应的置换函数的基本流程,其中包含$R_f$轮的full state和$R_p$轮的partial state,其中$R_f$轮需要所有状态均经过$S$盒(S-Box)的置换,$R_p$轮只需要经过一个$S$盒的置换即可,图中的术语如下所示
- AddRoundConstants, denoted by ARC(·), 线性层,对每个codeword加上一个预先定义的数字;
- SubWords, denoted by S-box(·) or by SB(·), 非线性层,对每个codeword进行幂次运算,一般是$X^3$或$X^5$。其中,$X$是每个codeword。Plonky2采用$X^7$;
- MixLayer, denoted by M(·), 线性层,和预先定义的矩阵进行乘法操作。
2.1 Full Rounds变换
rust
#[inline]
fn full_rounds(state: &mut [Self; SPONGE_WIDTH], round_ctr: &mut usize) {
for _ in 0..HALF_N_FULL_ROUNDS { // 经过constant layer, SBOX和MDS
Self::constant_layer(state, *round_ctr); // 加上一个数字, 线性层
Self::sbox_layer(state); // X^3或X^5, 非线性层
*state = Self::mds_layer(state); // 矩阵乘法, 线性层
*round_ctr += 1;
}
}
// plonky2/src/hash/poseidon.rs上述代码展示了Poseidon hash的full rounds层对应的变换
2.2 Partial Rounds变换
rust
fn partial_rounds(state: &mut [Self; SPONGE_WIDTH], round_ctr: &mut usize) {
Self::partial_first_constant_layer(state);
*state = Self::mds_partial_layer_init(state);
for i in 0..N_PARTIAL_ROUNDS {
state[0] = Self::sbox_monomial(state[0]);
unsafe {
state[0] = state[0].add_canonical_u64(Self::FAST_PARTIAL_ROUND_CONSTANTS[i]);
}
*state = Self::mds_partial_layer_fast(state, i);
}
*round_ctr += N_PARTIAL_ROUNDS;
}
// plonky2/src/hash/poseidon.rs上述代码展示了Poseidon hash的partial rounds层对应的变换
2.3 Permutation全流程
rust
#[inline] // Poseidon hash的全流程
fn poseidon(input: [Self; SPONGE_WIDTH]) -> [Self; SPONGE_WIDTH] {
let mut state = input;
let mut round_ctr = 0;
Self::full_rounds(&mut state, &mut round_ctr);
Self::partial_rounds(&mut state, &mut round_ctr);
Self::full_rounds(&mut state, &mut round_ctr);
debug_assert_eq!(round_ctr, N_ROUNDS);
state
}
// plonky2/src/hash/poseidon.rs上述代码展示了Poseidon hash中对应的一轮permutation的全过程
3. Poseidon的吸入、置换、压缩
完整的Poseidon Hash结构如下所示:
- 吸收阶段(Absorb Phase):
hash_n_to_hash_no_pad函数负责读取输入数据,并通过与内部状态 XOR 后执行置换。
rust
fn hash_no_pad(input: &[F]) -> Self::Hash {
hash_n_to_hash_no_pad::<F, Self::Permutation>(input)
}
// plonky2/src/hash/poseidon.rs- 置换阶段(Permutation Phase):
PoseidonPermutation对应P,实现了每一轮置换,涵盖了全轮(Full Rounds)和部分轮(Partial Rounds)的步骤。
rust
pub struct PoseidonPermutation<T> {
state: [T; SPONGE_WIDTH],
}
// plonky2/src/hash/poseidon.rs- 压缩阶段(Squeeze Phase): 压缩阶段从内部状态中提取哈希结果。
rust
/// A one-way compression function which takes two ~256 bit inputs and returns a ~256 bit output.
pub fn compress<F: Field, P: PlonkyPermutation<F>>(x: HashOut<F>, y: HashOut<F>) -> HashOut<F> {
// TODO: With some refactoring, this function could be implemented as
// hash_n_to_m_no_pad(chain(x.elements, y.elements), NUM_HASH_OUT_ELTS).
debug_assert_eq!(x.elements.len(), NUM_HASH_OUT_ELTS);
debug_assert_eq!(y.elements.len(), NUM_HASH_OUT_ELTS);
debug_assert!(P::RATE >= NUM_HASH_OUT_ELTS);
let mut perm = P::new(core::iter::repeat(F::ZERO));
perm.set_from_slice(&x.elements, 0);
perm.set_from_slice(&y.elements, NUM_HASH_OUT_ELTS);
perm.permute();
HashOut {
elements: perm.squeeze()[..NUM_HASH_OUT_ELTS].try_into().unwrap(),
}
}
// plonky2/src/hash/hashing.rsrust
pub fn hash_n_to_hash_no_pad<F: RichField, P: PlonkyPermutation<F>>(inputs: &[F]) -> HashOut<F> {
HashOut::from_vec(hash_n_to_m_no_pad::<F, P>(inputs, NUM_HASH_OUT_ELTS))
}
// plonky2/src/hash/hashing.rscompress和hash_n_to_hash_no_pad实现了具体的吸收(absorb)和压缩(squeeze)。hash_n_to_hash_no_pad 会调用 PoseidonPermutation 进行内部状态的置换,并在合适的时间点进行数据的压缩。
特例:two_to_one 函数实现了类似 Merkle 树节点的哈希,它将两个哈希值(即两个叶子节点)进行合并,并生成新的哈希值,主要用于FRI构造Merkle Hash调用Poseidon Hash的过程。
rust
fn two_to_one(left: Self::Hash, right: Self::Hash) -> Self::Hash {
compress::<F, Self::Permutation>(left, right)
}
// plonky2/src/hash/poseidon.rs4. Goldilocks域 & Plonky2中Poseidon的优化
在Plonky2中,一般选取Goldilocks域作为有限域$F_p$,其中$p=2^{64}-2^{32}+1$,它可以将任何的witness/codeword转换为$64$位长的数,其主要具有以下优点:
- 目前的处理器处理$64$位长的数十分高效,因为它正好可以使用传统的bit string的处理方式来处理算术运算,比如乘以$2$或者除以$2$相当于移位操作;
- 在编写为算术电路时,因为Goldilocks域的操作均属于算术操作,所以无需对其进行模拟,相比于传统的基于二进制的SHA256哈希函数而言,该类哈希函数具有更小规模的电路和更少的约束个数。
Plonky2在MDS层使用的矩阵的第一行为$[1; 1; 2; 1; 8; 32; 2; 256; 4096; 8; 65536; 1024]$,其中每个元素都是2的幂次方,它使得算术电路中的乘法操作和二进制中的移位操作等价,极大地提高了运算效率,除此之外,矩阵中的每个元素值都比较小。
4.1 Poseidon的MDS运行过程
rust
fn mds_layer(state: &[Self; 12]) -> [Self; 12] {
let mut result = [GoldilocksField::ZERO; 12];
// Using the linearity of the operations we can split the state into a low||high decomposition
// and operate on each with no overflow and then combine/reduce the result to a field element.
let mut state_l = [0u64; 12];
let mut state_h = [0u64; 12];
for r in 0..12 {
let s = state[r].0;
state_h[r] = s >> 32;
state_l[r] = (s as u32) as u64;
}
// 使用优化的FFT进行运算
let state_h = poseidon12_mds::mds_multiply_freq(state_h);
let state_l = poseidon12_mds::mds_multiply_freq(state_l);
for r in 0..12 {
let s = state_l[r] as u128 + ((state_h[r] as u128) << 32);
// from_noncanonical_u96将输入的 96 位数据(
// (表示为一个 64 位的低位部分和一个 32 位的高位部分)转换为 Goldilocks 域
// 中的一个元素
result[r] = GoldilocksField::from_noncanonical_u96((s as u64, (s >> 64) as u32));
}
// Add first element with the only non-zero diagonal matrix coefficient.
let s = Self::MDS_MATRIX_DIAG[0] as u128 * (state[0].0 as u128);
result[0] += GoldilocksField::from_noncanonical_u96((s as u64, (s >> 64) as u32));
result
}
// plonky2/src/hash/poseidon_goldilocks.rs4.2 Poseidon在Goldilocks域上的运行过程
1. 初始化结果数组
rust
let mut result = [GoldilocksField::ZERO; 12];- 这里初始化了一个长度为$12$的
result数组,用于存储最终的 MDS 变换结果。初始值为GoldilocksField::ZERO。
2. 分离状态向量的高位和低位
rust
let mut state_l = [0u64; 12];
let mut state_h = [0u64; 12];
for r in 0..12 {
let s = state[r].0;
state_h[r] = s >> 32;
state_l[r] = (s as u32) as u64;
}state_l和state_h数组分别存储了状态向量中每个元素的低位和高位部分。- 通过位操作,
state_h存储元素的高$32$位,state_l存储低$32$位。
3. 用FFT加速MDS算法
rust
let state_h = poseidon12_mds::mds_multiply_freq(state_h);
let state_l = poseidon12_mds::mds_multiply_freq(state_l);- 这里调用
poseidon12_mds::mds_multiply_freq函数对state_h和state_l分别基于 FFT的 MDS 矩阵乘法,以加速矩阵乘法运算。
4. 合并高位和低位的结果
rust
for r in 0..12 {
let s = state_l[r] as u128 + ((state_h[r] as u128) << 32);
result[r] = GoldilocksField::from_noncanonical_u96((s as u64, (s >> 64) as u32));
}- 这里将高位和低位部分重新组合为$96$位整数。
state_h部分左移$32$位后与state_l相加,得到完整的$96$位数值。 - 然后调用
GoldilocksField::from_noncanonical_u96将这个$96$位整数转换为 Goldilocks 域内的元素,并存储到result中。
5. 添加对角矩阵的一个非零元
rust
let s = Self::MDS_MATRIX_DIAG[0] as u128 * (state[0].0 as u128);
result[0] += GoldilocksField::from_noncanonical_u96((s as u64, (s >> 64) as u32));- 最后,为了完成 MDS 变换的对角部分,函数将
MDS_MATRIX_DIAG[0]和state[0]相乘后添加到result[0]中。
- 学分: 18
- 分类: 密码学基础
- 标签:
